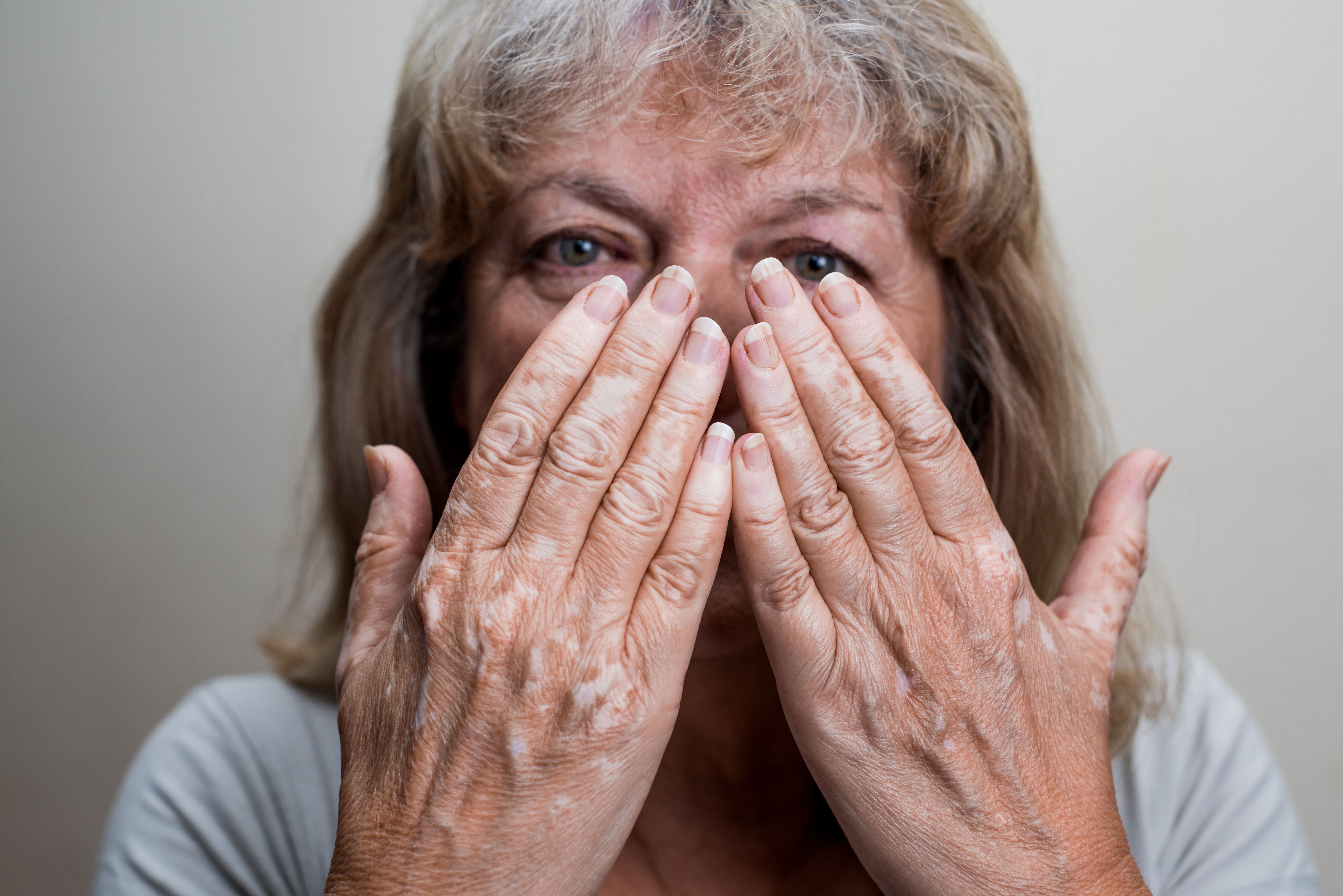
A recent study has revealed 135 previously unknown genes that play important roles in regulating melanin production in humans—and that could lead to melanin-modifying drugs for vitiligo and other pigmentation diseases.
The research team was led by Vivek Bajpai, assistant professor in the School of Sustainable Chemical, Biological and Materials Engineering at the University of Oklahoma, with collaborators from Stanford University, where Bajpai did postdoctoral work.
Melanin synthesis is compartmentalized within the melanosome, in specialized pigment cells (melanocytes). The synthesis of melanin within the melanosomes varies, which is why human skin, hair, and eye color vary. Pigmentation-related diseases are associated with disruptions in melanogenesis.
Melanin’s particular physicochemical properties, such as high refractive index, determine its optical properties, the researchers wrote in their article, published in Science on Aug. 11. “We reasoned that an accumulation of melanin within melanosomes would change melanocytes’ light-scattering properties.”
Bajpai developed a novel method to detect and quantify the melanin-producing activity of melanocytes: Passing light through the melanocytes, he could record whether the light was absorbed or scattered by the melanin. “If there are a lot of melanin-producing melanosomes,” he said in a University of Oklahoma press release, “the light will scatter much more than in cells with little melanin.”
The team measured light scattering through flow cytometry, capturing “dynamic shifts” in melanin levels within melanosomes. They used CRISPR-Cas9 technology to genetically engineer cells, and conducted a genome-wide genetic screen, systematically removing more than 20,000 genes from hundreds of millions of melanocytes.
Their screen identified 169 genes, including some that were previously known and 135 new melanin-promoting genes whose deletion was associated with reduced light scattering—in other words, loss of melanin.
The melanin-promoting genes are involved in diverse biological pathways, such as transcription regulation, RNA processing, and endosomal transport, the researchers say. “Consistent with their melanin-promoting role, the expression of the majority of our screen hits is elevated in darkly pigmented, compared with lightly pigmented, human melanocytes. Our analyses revealed that select melanin-promoting genes are associated with skin color variation and show evidence of local adaptation in human populations.”
By focusing on specific previously unidentified candidates, the researchers say, “we implicated a new cargo recycling pathway in melanosome function and identified a transcription factor involved in melanosome maturation. Our work provides a rich resource for further studies of melanogenesis and its relationship with skin color variation and human diseases.”
Their findings are also meaningful to a broad swath of science beyond dermatology. Bajpai’s method of targeting melanin-producing genes could lead to prevention of fungi- and bacteria-related diseases in humans and crops.
Reference: https://www.managedhealthcareexecutive.com/view/newly-discovered-genes-could-change-vitiligo-treatment